

Not Null Constraint: Not Null: If this option Not Null Constraint: Name: Name for the Not Requires values in a column to comply with a specified condition. For more details, see the Identity Columnĭisplays the Not Null and Check Constraints for a column. This is applicable only for Oracleĭatabase 12c and later releases. Identity Column: If this option is selected, PK: If this option is selected, the column Use this field to provide descriptions for the attributes. Inserted into the table and the value specified for the column is NULL, theĭefault value is inserted into the column.Ĭomments: Optional descriptive comments about If this option is selected, when a row is Value inserted into the column when a row is inserted.ĭatabase 12c and later releases. After you have created a database link, you can use it to refer to tables and views in the other database.ĭescription of "Figure 3-17 Add a Column"ĭefault: If no value is specified, the default Synonyms, Public Synonyms: Synonyms provide alternative namesįor tables, views, sequences, procedures, storedįunctions, packages, materialized views, JavaĬlass database objects, user-defined object types,ĭatabase Links: A database link is a database object in one database that enables you to access objects on another database. The materialized view log to refresh materialized When DML changes are made to master tableĭata, Oracle Database stores rows describing thoseĬhanges in the materialized view log and then uses Materialized Views Logs: A materialized view log is a tableĪssociated with the master table of a materialized The FROMĬlause of the query can name tables, views, and Materialized View: A materialized view is a database object You can use sequences to automatically generate Sequences: Sequences are used to generate unique integers. Types: A data type associates a fixed set of properties with the values that can be used in a column of a table or in an argument of a function or procedure. Triggers: Triggers are stored PL/SQL blocks associated with a table, a schema, the database, or anonymous PL/SQL blocks or calls to a procedure implemented in PL/SQL or Java.
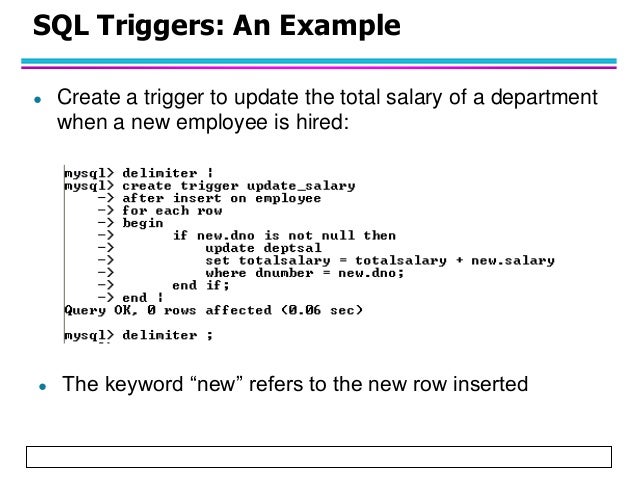
#Duplicate column name foreign key sqleditor code#
Select Run from the context menu to insert the code for a selected function, procedure, or package into the worksheet. A package can contain functions or procedures, or both. Packages, Functions, Procedures: A package contains subprograms, which are programming objects that can be stored and executed in the database server, and called from other programming objects or applications. Indexes: An index contains an entry for each value thatĪppears in the indexed column of the table and Views: Views are virtual tables that select data from one or The object name and any other aspects of theĭefinition, as needed, to create a new object of Or you can selectĭisplays the dialog box with information for the You can create new tables, edit existing tables, and add indexes by using the optionsĪvailable in the context menu. Each table has multiple columns that describe the attributes of the database entity associated with the table, and each column has an associated data type. The various object types and the corresponding options are: Statements for creating the object to a worksheet or to a text file. For all objects, the context menu includes If you do not have any existing objects for a object type (such as tables), you canĬreate objects by using the Object submenu icon, after first selecting the object type from theĭrop-down list. The Materialized View Log Properties Dialog The wizards for creating and editing various object types are Object wizards available from the Navigator tab in the SQL and Data Modeler You can create and edit objects using Create and Edit


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
